Project: Visual exploration of segmentation errors in pelvic structures
Description
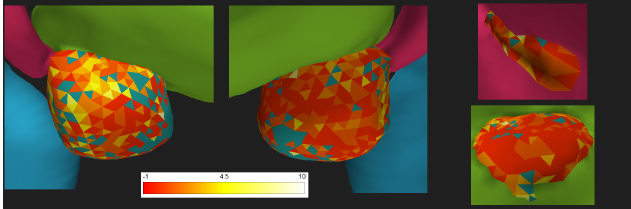
Nowadays, the usage of medical imaging data is widely present in both diagnostic procedures and treatment planning. Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computer Tomography (CT) scans, sets of two-dimensional slices are obtained, from which three-dimensional models can be constructed using segmentation algorithms. These three-dimensional models are frequently used in addition to the two-dimensional slices, to provide insights in the physical properties of the organs such as shape, size and relative position in an intuitive way. This information is, amongst others, used by medical specialists in radiotherapy treatment planning to determine the exact location and dose of radiation required to treat cancer patients.
For the inspection of the organs physical properties, it is essential that the results from the segmentation algorithm are accurate and reliable. Using the data originating from the segmentation algorithm, the quality of the resulting meshes can be assessed. On the one hand, this allows users to confirm the quality of a single mesh, ensuring that this mesh is suitable for use by clinical users. On the other hand, quality analysis allows technical researchers such as computer scientists working on the segmentation algorithm to identify weaknesses in the segmentation phase, allowing them to improve the algorithm. Currently, there is no system available which provides the tools for users to obtain this required information yet. Therefore, the process of studying the available patient data is complex and time consuming.
This document contains the design decisions made in the development of a web-based visualization framework for three-dimensional model inspection and multivariate data inspection and correlation detection in the segmentations of pelvic structues. It documents the requirements for such an application, provides context in terms of the current state of the art, and discusses the resulting framework.
Details
- Student
-
FMFreek Marcelis
- Supervisor
-
 Huub van de Wetering
Huub van de Wetering
- Secondary supervisor
-
 Anna Vilanova
Anna Vilanova
- Link
- Thesis